html
Autonomous Driving Safety: The Real Challenges of Technical Defects and Liability Dilemmas
While technology enthusiasts hail autonomous driving as a revolutionary leap, real-world incidents continue to expose critical vulnerabilities in this “future-ready” technology. Stay informed as we dissect the three major technical flaws plaguing autonomous systems, uncover how automakers evade accountability, and provide actionable safety tips. Whether you’re a tech professional or a daily driver, this guide will empower you with insights to navigate the complexities of autonomous driving safely.
1. Three Major Technical Defects of Autonomous Driving Systems

1.1 Visual Blind Spots: Unidentified Dangers
A 2023 Shenzhen incident highlighted a parked vehicle colliding with a fire hydrant, revealing:
- Obstacles under 30 cm (e.g., curbs) often go undetected.
- Reflective surfaces (e.g., glass facades) mislead sensors.
- Non-standard objects (e.g., temporary barriers) lack recognition.
Experts note: “Current visual systems match a 5-year-old’s cognitive ability, faltering in complex environments.”
1.2 Algorithm Vulnerabilities: Fatal Misjudgments
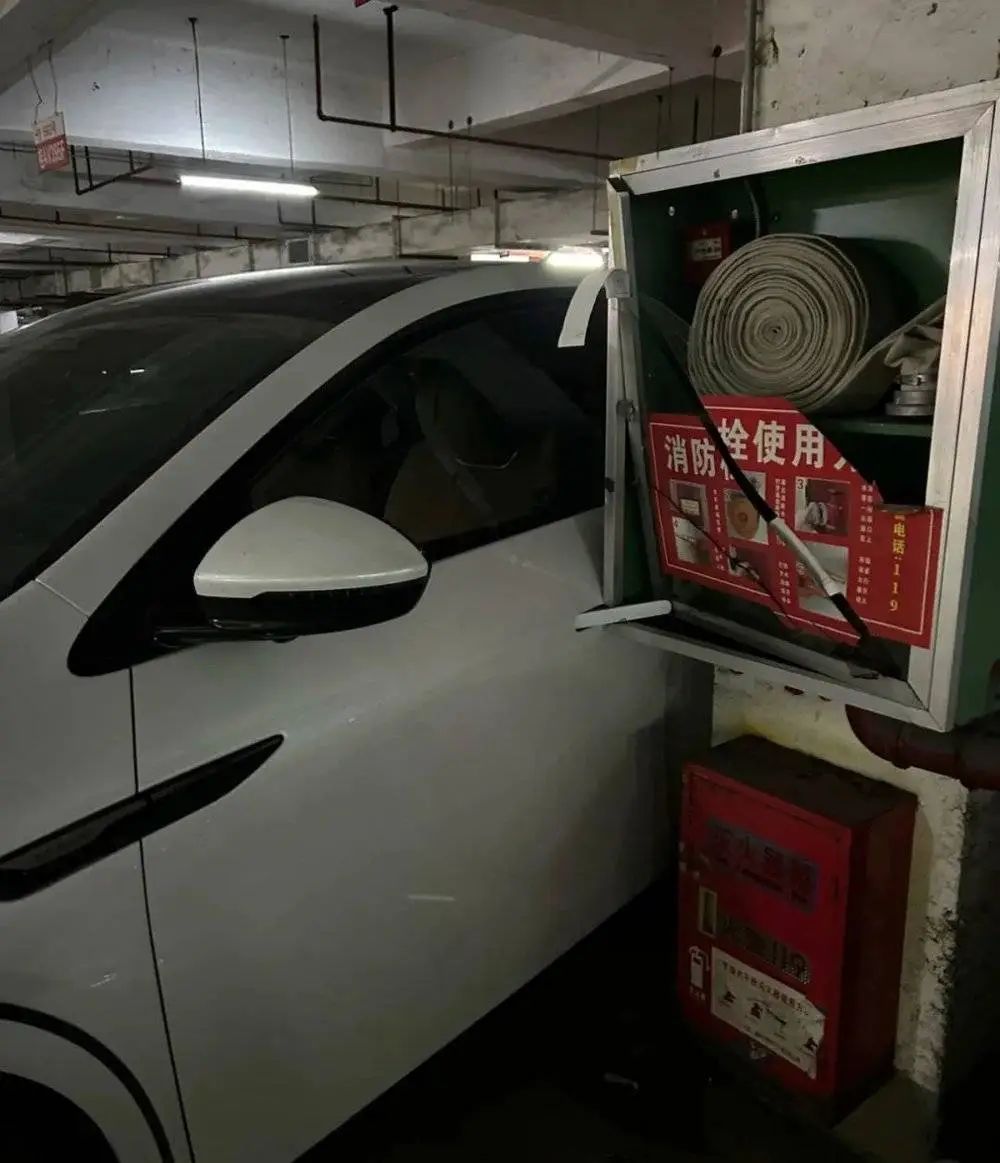

Mr. Guo’s highway scare exposed:
- Over-reliance on outdated high-definition maps.
- Prioritization of speed over safety protocols.
- No contingency plans for sudden road changes.
Emergency response error rates reach 12%—six times higher than human drivers.
1.3 Human-Machine Conflict: Dangerous Handover Gaps
Ms. Chen’s collision revealed:
- 0.3-second reaction windows vs. human averages of 1.2 seconds.
- Contradictory liability clauses in user agreements.
- “Ready to takeover” claims rarely hold in practice.
90% of drivers fail to respond effectively during sudden system disengagements.
2. Automakers’ Evasion Tactics
2.1 Marketing vs. Reality Gaps
Common deceptive practices include:
- Misleading terms like “L2.999” implying full autonomy.
- Post-accident “feature disabling” via software updates.
- Unilateral user agreement modifications.
2.2 Legal Loophole Strategies
Standardized accident response playbook:
- Classify all incidents as L2 “driver-assist” events.
- Invoke exemption clauses in user contracts.
- Cite lack of industry standards as defense.
2022 data shows automakers avoided liability in 83% of lawsuits.
3. Consumer Rights Struggles
3.1 Proof Burden Obstacles
- Data access controlled exclusively by manufacturers.
- No standardized accident investigation protocols.
- $35,000 average legal costs deter pursuit.
3.2 Compensation Disparities
- Fatal autonomous accidents: ~$119,000 settlements.
- Equivalent traditional accidents: $280,000 averages.
- “Goodwill” payments: Rarely exceed $14,000.
4. Safety Improvement Roadmap
4.1 Technical Upgrades
Priority innovations:
- Multi-sensor fusion systems (camera+radar+lidar).
- Triple-redundant safety algorithms.
- 3-second pre-warning human-machine interfaces.
Haptic feedback systems improve takeover success by 40% in tests.
4.2 Legal Reforms
Urgent needs:
- Mandatory data transparency platforms.
- Autonomy-level-based insurance pricing.
- Dynamic liability frameworks.
Germany now holds manufacturers fully liable during L3 activation.
5. Consumer Protection Guidelines
5.1 Purchase Precautions
- Verify SAE autonomy levels.
- Scrutinize user agreement sections 5-8.
- Demand emergency takeover demonstrations.
5.2 Usage Safety Rules
- Maintain hands-on-wheel posture.
- Practice emergency braking routines.
- Avoid complex roads in assist modes.
Proper usage reduces accident risks by 65% according to studies.
6. Industry Trend Forecast
6.1 Tech Milestones
Projected timeline:
- 2025: L3 limited commercial deployment.
- 2028: Full highway automation.
- 2035: Urban mixed driving normalization.
*May delay by 2-3 years based on R&D progress.
6.2 Regulatory Progress
- China: 2024 autonomous accident standards trial.
- USA: 2025 mandatory data recorders.
- EU: 2026 unified liability framework.
Conclusion: Balancing Innovation & Caution
Autonomous driving remains in developmental stages requiring:
- Constant human supervision for L2 systems.
- Skepticism toward “full autonomy” claims.
- Meticulous record-keeping.
Technological progress must prioritize human safety. Stay informed through biannual safety training to enjoy technology responsibly.
